202406262119
Status:
Tags: ECG
Wellens syndrome
-
Pattern of T-wave abnormality in mid precordial leads (V2-V3, +/- V4)
-
No loss of R-waves in precordial leads
-
Highly specific for critical obstruction of the proximal LAD
-
High risk for extensive anterior wall MI and death
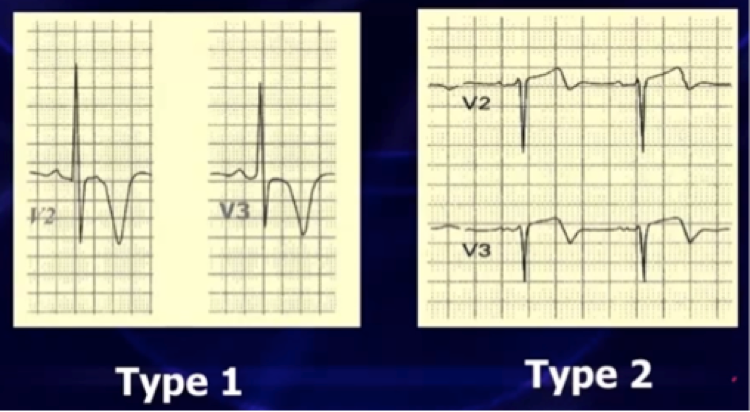
-
Type 1 – Deeply symmetric TWI
-
Type 2 – Biphasic T waves with terminal TWI. Goes up first, then down (often misdiagnosed as “normal” or “non-specific T-wave abnormality”). Often misdiagnosed as “non-specific T-wave pattern” or “normal”.
-
ST changes are often absent and patient can be in a chest pain free state!
-
Cardiac biomarkers often initially normal
-
Best to diagnose in absence of high voltage
-
Not currently a guideline indication for cath or lytics (especially when pain free without STE) but…
-
Medical management usually ineffective and patients are best treated with PCI, treadmill stress testing may be hazardous and precipitate acute MI.
-
Patients will have anterior wall MI unless they get early PCI. 75% developed acute MI within weeks when only medically managed.
-
Get serial ECG’s, as some of these do evolve into STEMI in the ED
-
Watch carefully for Wellens’ as some of your consultants may not know about this.
DDx
normal variant ST elevation & TWI
- Young males, especially athletes
- Typically of African-Caribbean descent